Birmingham is leading the way in SMART building development, integrating advanced technologies like IoT, BIM, and AI to create efficient and tech-friendly spaces. Two standout projects, Enterprise Wharf and Three Chamberlain Square, highlight these efforts:
- Enterprise Wharf: Features automated systems for lighting, heating, and ventilation, energy-saving designs, and real-time data insights via a mobile app. It's popular with tech start-ups and offers flexible workspaces.
- Three Chamberlain Square: Part of the Paradise regeneration scheme, it includes solar panels, rainwater harvesting, AI-driven operations, and wellness tech. It has attracted major tech companies and offers co-working spaces.
These innovations are reshaping Birmingham’s commercial landscape, attracting tech professionals and businesses. The city's focus on SMART infrastructure aims to boost efficiency, connectivity, and sustainability while addressing challenges like cybersecurity and skills gaps. With over 2,000 tech start-ups and a growing talent pool, Birmingham is positioning itself as a key player in the UK's digital economy.
Diatomic Digital Twin: Transforming Birmingham’s Urban Future
Major SMART Building Projects in Birmingham
Birmingham has established itself as a frontrunner in the development of SMART buildings, showcasing projects that are redefining commercial spaces. These initiatives not only reshape the city's skyline but also create inviting environments for innovative businesses and tech professionals. Here are two standout examples of Birmingham's forward-thinking approach to intelligent building design.
Enterprise Wharf
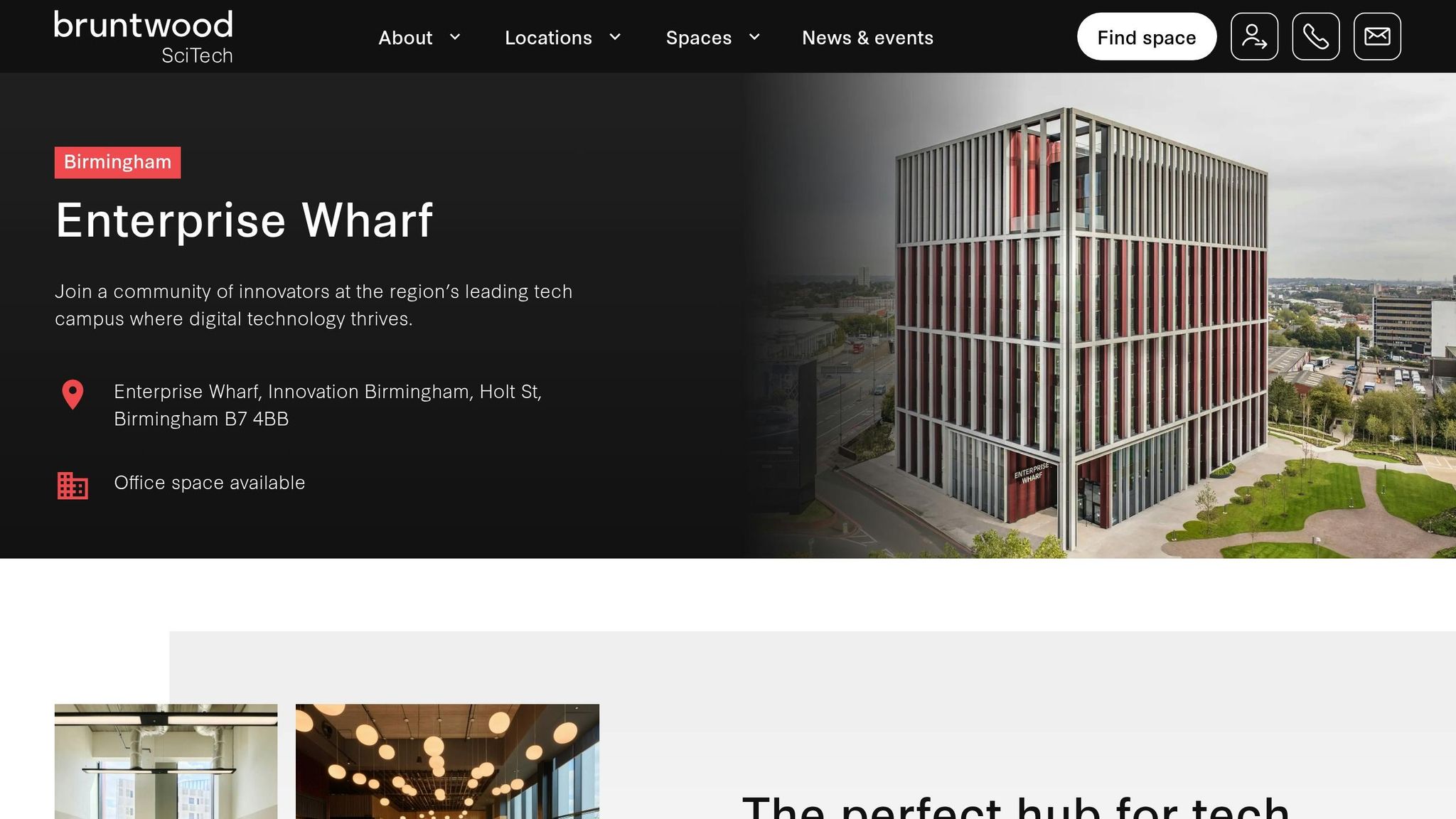
Enterprise Wharf is a prime example of Birmingham's SMART building innovations, situated in the city's bustling business district along the historic canal network. This mixed-use development has set a high standard for intelligent design in the West Midlands.
The building features advanced management systems that automatically adjust lighting, heating, and ventilation based on occupancy levels and external weather conditions. Energy efficiency is prioritised with features such as energy-saving glazing, high-performance insulation, and a green roof system that manages rainwater runoff while providing natural cooling. Its digital infrastructure includes high-speed fibre connectivity and dedicated tech zones, enabling data-heavy operations. Tenants also benefit from real-time insights into energy consumption, air quality, and space usage via a mobile app.
Enterprise Wharf has become a magnet for tech start-ups and growing businesses, with many of its offices occupied by technology firms. Its flexible workspace design supports evolving business needs, featuring modular meeting rooms and collaborative spaces that can be booked through integrated digital platforms.
Three Chamberlain Square
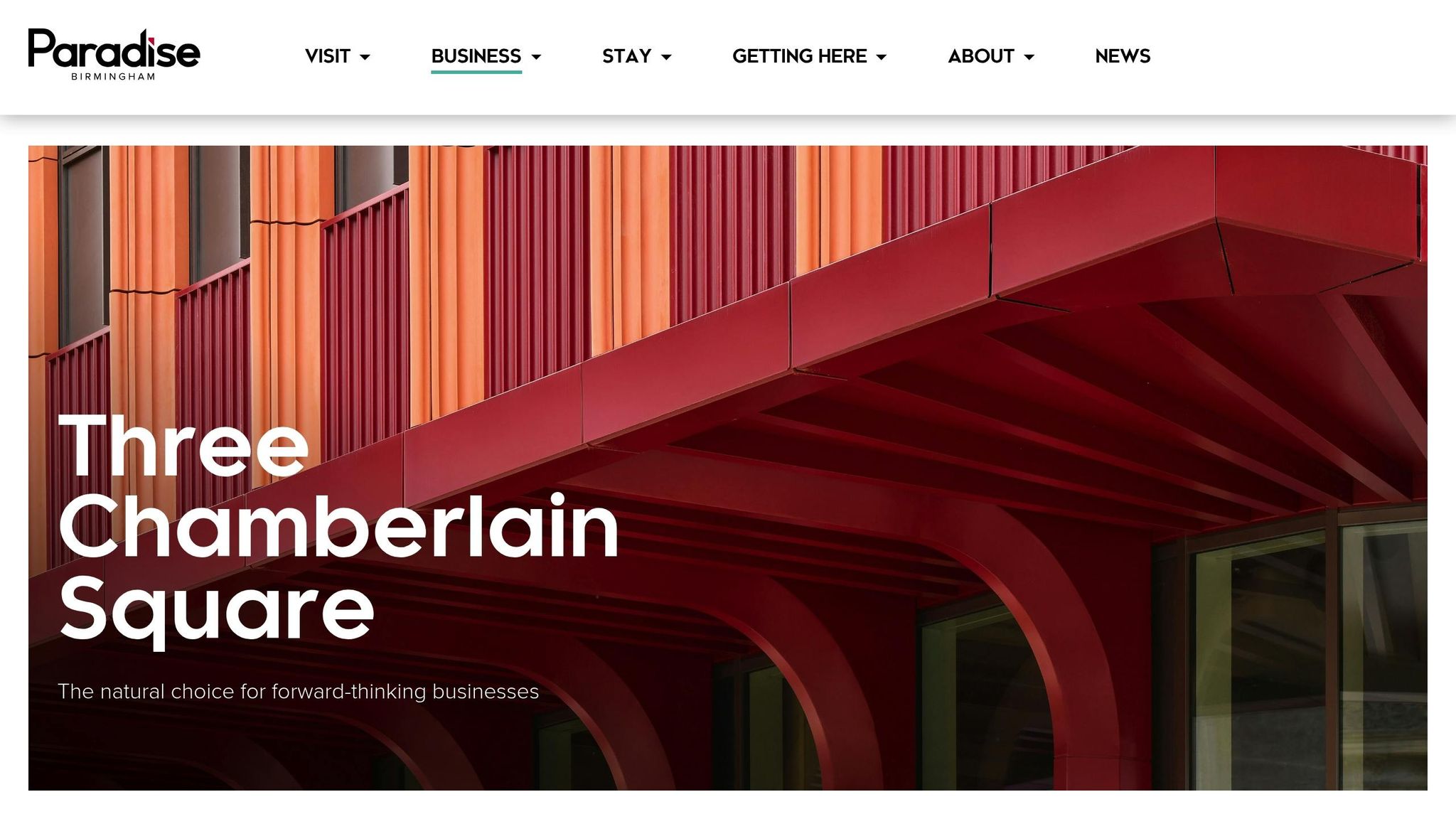
Three Chamberlain Square is another ambitious SMART building project, forming part of Birmingham's expansive Paradise regeneration scheme. This development blends Grade A office spaces with retail and hospitality offerings, all interconnected through advanced digital systems.
The building has earned BREEAM Outstanding certification by adhering to rigorous environmental standards. Solar panels on the roof supply part of its energy needs, while rainwater harvesting systems help reduce the use of mains water.
Digital integration at Three Chamberlain Square goes beyond standard building management. Smartphone-accessible services allow users to book facilities, while AI systems optimise operations to enhance efficiency. Wellness technology also plays a role, monitoring air quality and offering circadian lighting to promote occupant wellbeing.
The building has already attracted several major technology companies as tenants, highlighting its appeal to the tech industry. Its advanced telecommunications infrastructure, including 5G connectivity and secure server rooms, further boosts its attractiveness. Flexible co-working spaces also cater to freelancers and small tech teams, fostering a dynamic and innovative community.
These projects demonstrate how SMART technologies are transforming Birmingham into a hub for efficient, sustainable, and tech-friendly workspaces, solidifying its position as a leading tech city outside London.
Technologies Used in Birmingham's SMART Buildings
Birmingham's commercial properties are increasingly integrating three key technologies - IoT (Internet of Things), BIM (Building Information Modelling), and AI with digital twins - to create spaces that are adaptive, efficient, and smarter than ever.
Internet of Things (IoT) for Automation
IoT plays a pivotal role in making buildings responsive and efficient. At Enterprise Wharf, for instance, thousands of IoT sensors monitor factors like occupancy, air quality, temperature, humidity, and lighting. These sensors trigger automatic adjustments to improve comfort while reducing energy consumption.
The impact of IoT is significant. It can cut maintenance costs by 20–30% and energy use by 15–30%. Additionally, IoT systems reduce equipment downtime by 30–50%, ensuring smoother operations.
One standout application is air quality monitoring. IoT sensors track CO₂ levels, particulate matter, and volatile organic compounds. When air quality dips below optimal thresholds, ventilation systems automatically adjust to improve the workspace environment. This is especially crucial in offices where employees spend long hours, promoting a healthier and more productive atmosphere.
IoT also enhances space management by analysing occupancy patterns. For example, it can pre-adjust environmental controls during peak usage times, ensuring spaces are always ready for their intended purpose.
Building Information Modelling (BIM)
BIM transforms how buildings are designed and managed by creating detailed digital models. During the planning of Three Chamberlain Square, architects used BIM software to simulate environmental scenarios, model airflow, and predict energy needs. This allowed them to determine the best placement for IoT sensors, ensuring maximum efficiency.
Beyond the design phase, BIM remains an essential tool throughout a building's lifecycle. Its 3D models help maintenance teams locate pipes, cables, and sensors quickly, simplifying renovations and repairs. BIM also prevents costly delays by identifying clashes between building systems early in the process. This clash detection ensures smoother collaboration across construction teams.
AI and Digital Twins
AI and digital twins take building intelligence to the next level by enabling real-time optimisation and predictive maintenance. Digital twins act as virtual replicas of buildings, reflecting their real-time performance. They process thousands of data points every minute, allowing managers to see how factors like occupancy or weather impact operations without making physical changes.
AI adds another layer of functionality by analysing this data to forecast needs. For example, it can detect patterns in room occupancy and adjust cooling systems proactively. In server rooms, AI can anticipate increased cooling demands during warmer weather, ensuring critical systems remain operational.
Predictive maintenance is another game-changer. Instead of sticking to fixed schedules, AI monitors equipment performance and flags early signs of wear. This reduces the risk of unexpected failures and extends the lifespan of key components. Machine learning algorithms also identify inefficiencies, such as unnecessary energy use in specific areas, and suggest corrective actions.
Digital twins further assist with scenario planning. Managers can test potential changes - like adding equipment or altering layouts - virtually, assessing their impact on energy use, comfort, and costs before making any physical adjustments.
sbb-itb-1ad140f
How SMART Buildings Affect Birmingham's Tech Sector
Birmingham's shift towards SMART buildings is transforming its tech scene. These advanced structures go beyond improving energy efficiency and automation - they're creating workspaces that prioritise both sustainability and employee wellbeing. By doing so, they're becoming magnets for skilled professionals seeking cutting-edge, environmentally conscious environments.
Attracting and Keeping Talent
Tech professionals increasingly look for workspaces that cater to their needs. SMART buildings meet this demand with features like automated controls and real-time monitoring, allowing individuals to customise settings such as lighting and temperature to their preferences. This personalisation creates a more engaging and comfortable work experience. Additionally, the sustainability features of these buildings appeal strongly to professionals who value eco-conscious practices. By offering a blend of comfort and environmental responsibility, SMART buildings enhance a company's reputation and make it easier to attract and retain talent that aligns with these values.
Role of Connecting Birmingham
As these advanced workspaces become the norm, connecting talent with forward-thinking employers is more important than ever. Platforms like Connecting Birmingham play a key role here, linking job seekers with organisations that embrace SMART building technologies. The platform offers curated job listings and detailed profiles that showcase company culture, team dynamics, and workspace capabilities. By spotlighting employers who invest in modern, sustainable environments, Connecting Birmingham helps professionals make informed career choices while giving businesses access to tech-savvy individuals who value innovation and sustainability.
Future SMART Infrastructure Plans for Birmingham
Birmingham is setting its sights on expanding SMART building technologies, aiming to weave advanced digital systems into the fabric of its urban infrastructure. These forward-thinking plans are designed to create more efficient and connected environments, supporting the city's flourishing tech and creative industries. Building on existing successes, this approach positions Birmingham for a future driven by data and innovation.
Planned SMART Building Projects
Local agencies are gearing up to roll out projects that embed SMART systems across the city. The vision? A fully interconnected urban ecosystem where buildings communicate seamlessly with each other and the wider network. These developments could include features like automated management systems, cutting-edge digital controls, and enhanced connectivity - all tailored to boost commercial activity and meet the demands of a modern, tech-focused economy. By extending the benefits of current SMART buildings, these projects aim to take Birmingham’s infrastructure to the next level.
Opportunities and Challenges
The expansion of SMART infrastructure opens the door to exciting opportunities for local businesses. Tech firms, for instance, could enjoy more streamlined operations and improved connectivity, making remote collaboration and cloud-based services easier than ever. Digital agencies might also benefit, using integrated data analytics to optimise workspace usage and fine-tune their operational strategies.
But it's not all smooth sailing. The interconnected nature of SMART systems introduces cybersecurity risks, meaning robust protection measures and comprehensive staff training will be essential. Another hurdle is the skills gap - balancing traditional expertise with emerging digital know-how will be critical for the successful deployment and maintenance of these systems. Initial investment costs could also be a barrier, while evolving regulations around data protection and environmental standards demand strict compliance.
Despite these challenges, insights from similar initiatives suggest that the long-term advantages - like greater operational efficiency and a competitive edge - could far outweigh the initial difficulties. For businesses in Birmingham, embracing these technologies early could pave the way for thriving in an increasingly digital landscape.
Conclusion
Birmingham is undergoing a significant transformation, blending cutting-edge technology with urban development. With initiatives like Enterprise Wharf and Three Chamberlain Square, the city is embracing IoT, digital twins, and AI-driven automation to redefine its tech and economic landscape.
The impact is evident. Birmingham now boasts over 2,000 tech startups and 6,000 tech companies. Its digital economy is thriving, with venture capital investment doubling in 2023, a £50 million commitment from Bruntwood SciTech, and the addition of 20 new tech-driven businesses in 2024.
For those seeking opportunities, platforms like Connecting Birmingham play a crucial role in linking local talent with employers operating from these advanced SMART buildings.
With a robust pipeline of 132,000 West Midlands students specialising in computer science and engineering, Birmingham is positioning itself as a leader in digital innovation across the UK.
FAQs
How do SMART buildings like Enterprise Wharf and Three Chamberlain Square promote sustainability and energy efficiency in Birmingham?
SMART buildings like Enterprise Wharf and Three Chamberlain Square are at the forefront of promoting sustainability and energy efficiency in Birmingham. By incorporating advanced energy-saving technologies and environmentally conscious designs, these buildings help minimise resource use and lessen their impact on the planet.
A prime example is Three Chamberlain Square, which has achieved a BREEAM Outstanding rating and a NABERS UK 5-star rating - clear evidence of its dedication to sustainable practices. These initiatives are closely tied to Birmingham’s ambitious target of reducing carbon emissions by 50% by 2030, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable cityscape.
How do technologies like IoT, BIM, and AI contribute to the development and management of SMART buildings in Birmingham?
Technologies like IoT (Internet of Things), BIM (Building Information Modelling), and AI (Artificial Intelligence) are reshaping Birmingham’s SMART buildings, making them more efficient, functional, and environmentally friendly.
With IoT sensors, systems such as heating, lighting, and air quality are monitored in real time. This allows for smarter energy use and helps create healthier indoor environments. At the same time, AI processes this data to fine-tune building operations, anticipate maintenance needs, and minimise waste. BIM ties it all together by offering detailed digital models that guide better decision-making throughout a building’s lifecycle.
These advancements are steering Birmingham towards urban spaces that are not only more connected but also smarter and more sustainable.
What challenges does Birmingham face in expanding its SMART infrastructure, and how can these be overcome to ensure its success?
Birmingham faces a range of hurdles in building its SMART infrastructure. These include the challenge of bringing together diverse systems, securing the necessary funding to modernise utilities and transport networks, and ensuring that public safety measures evolve alongside technological progress.
Addressing these challenges calls for careful planning, increased financial resources, and solutions designed to grow and adapt over time. Success will depend on strong collaboration between local authorities, private sector partners, and the wider community. By encouraging innovation and implementing progressive policies, Birmingham has the potential to establish a resilient SMART infrastructure that serves both its residents and businesses effectively.


